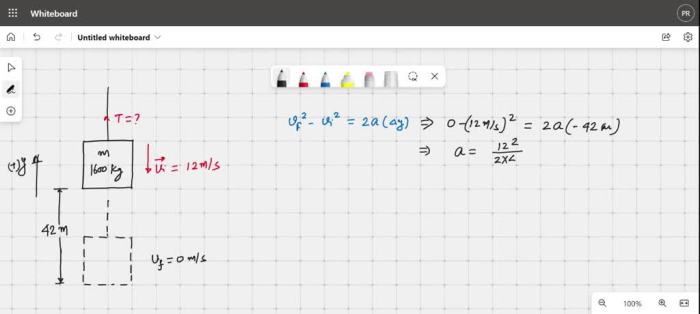
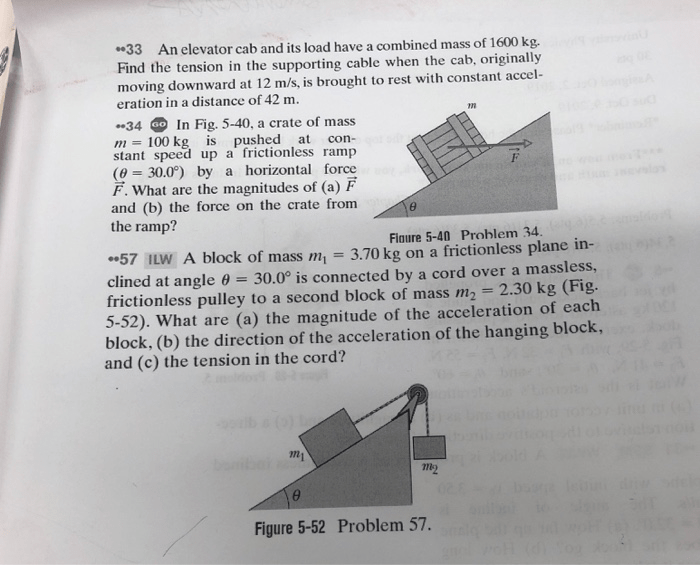
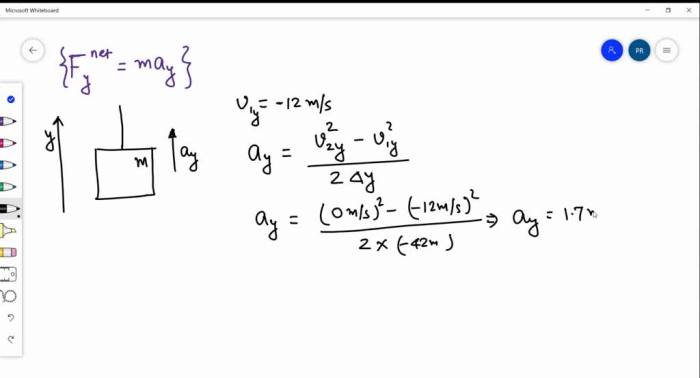
An elevator and its load have a combined mass of, presenting a captivating interplay of mass and force within a dynamic vertical transportation system. This article delves into the intricacies of elevator mechanics, exploring the relationship between mass, force, and the safety measures in place to ensure passenger well-being.
From the impact of gravity on elevator dynamics to the role of counterweights in balancing the load, this comprehensive guide unravels the complexities of elevator systems, highlighting their efficiency, reliability, and the advancements in automation that enhance passenger experiences.
Elevators: A Comprehensive Overview: An Elevator And Its Load Have A Combined Mass Of
Elevators are essential components of modern buildings, providing convenient and efficient vertical transportation. Understanding the principles of elevator operation, from mass and force interactions to control systems and safety measures, is crucial for their effective design, maintenance, and operation.
1. Mass and Force
Mass and force are fundamental concepts in elevator systems. Mass is a measure of an object’s resistance to acceleration, while force is an external influence that can change an object’s motion. In an elevator, the combined mass of the elevator car and its load determines the force required to lift it.
The force required to lift an elevator is directly proportional to its mass. This means that heavier elevators require more force to move than lighter ones. Gravity also plays a significant role in elevator systems, as it exerts a downward force on the elevator and its load.
2. Load Capacity and Safety
Load capacity refers to the maximum weight that an elevator can safely transport. It is determined by factors such as the strength of the elevator car, cables, and motor. Exceeding the load capacity can lead to overloading, which can compromise safety and damage the elevator system.
Various safety measures are implemented in elevators to prevent overloading and ensure passenger safety. These include weight sensors, overload switches, and emergency stop buttons. These systems monitor the load and automatically stop the elevator if it exceeds the safe capacity.
3. Counterweights and Balance
Counterweights are an essential component of elevator systems. They are weights attached to the opposite end of the elevator cables and serve to balance the load. Counterweights help reduce the energy consumption required to lift the elevator and its load, as they offset the weight of the car.
Different types of counterweights are used in elevators, including concrete blocks, steel weights, and hydraulic systems. The type of counterweight used depends on the elevator’s design and capacity.
4. Motor and Drive Systems
Motors are the driving force behind elevators. They generate the torque necessary to lift the elevator car and its load. Various types of motors are used in elevators, including electric motors, hydraulic motors, and traction motors.
The efficiency and reliability of the motor and drive system are crucial for elevator performance. Factors such as motor size, power, and control systems influence the elevator’s speed, acceleration, and energy consumption.
5. Control Systems and Automation, An elevator and its load have a combined mass of
Control systems are responsible for operating elevators safely and efficiently. They include sensors, feedback mechanisms, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) that monitor and regulate the elevator’s movement.
Advanced elevator control systems utilize automation to enhance passenger experience. Features such as destination dispatching, predictive algorithms, and remote monitoring improve elevator efficiency, reduce wait times, and provide a smoother and more comfortable ride.
6. Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection are essential for ensuring elevator safety and reliability. Maintenance procedures include cleaning, lubrication, and component replacement to prevent breakdowns and extend the elevator’s lifespan.
Safety inspections are conducted to verify the elevator’s compliance with safety standards and regulations. These inspections include testing emergency systems, checking for wear and tear, and ensuring the elevator is operating within safe parameters.
Query Resolution
What factors influence the load capacity of an elevator?
Load capacity is determined by the strength of the elevator’s cables, the capacity of the motor, and the size of the elevator car.
How do counterweights help elevators operate more efficiently?
Counterweights balance the weight of the elevator car, reducing the amount of energy required to lift it.
What safety measures are in place to prevent elevator overloading?
Elevators are equipped with sensors that detect when the car is overloaded and prevent it from moving.