Principles of microeconomics 10th edition n gregory mankiw free – Principles of Microeconomics, 10th Edition by N. Gregory Mankiw is an authoritative and comprehensive guide to the fundamental concepts and principles of microeconomics. This highly acclaimed textbook provides a clear and engaging introduction to the field, making it an invaluable resource for students, educators, and professionals alike.
Through its in-depth analysis and real-world examples, Principles of Microeconomics offers a thorough understanding of how individuals and firms make decisions in the marketplace. It explores various market structures, consumer behavior, production and costs, perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly, monopolistic competition, market failures, and the role of government intervention.
1. Introduction
Microeconomics is a branch of economics that focuses on the behavior of individual entities, such as consumers, firms, and households, in decision-making and the allocation of resources. The 10th edition of N. Gregory Mankiw’s “Principles of Microeconomics” provides a comprehensive overview of microeconomic principles, theories, and applications, with updated content and examples to reflect the latest economic developments.
2. Market Structures
Perfect Competition
Perfect competition is a market structure characterized by numerous buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, perfect information, and freedom of entry and exit. In a perfectly competitive market, no single buyer or seller has market power, and the equilibrium price and quantity are determined by the interaction of supply and demand.
Monopoly
A monopoly is a market structure in which there is only one seller of a unique product. Monopolists have market power and can set prices above marginal cost, leading to higher prices and lower output compared to perfect competition.
Oligopoly
Oligopoly is a market structure with a small number of large firms that control a significant portion of the market. Firms in an oligopoly are interdependent and their decisions affect each other’s profits.
Monopolistic Competition, Principles of microeconomics 10th edition n gregory mankiw free
Monopolistic competition is a market structure characterized by many small firms that produce differentiated products. Firms in monopolistic competition have some market power but face competition from similar products.
3. Consumer Behavior

Consumer Preferences and Utility
Consumer preferences represent the choices that consumers make between different goods and services. Utility is a measure of the satisfaction or benefit that consumers derive from consuming goods and services.
Factors Influencing Consumer Demand
Consumer demand is influenced by various factors, including income, prices, tastes, and expectations. Changes in these factors can lead to shifts in the demand curve.
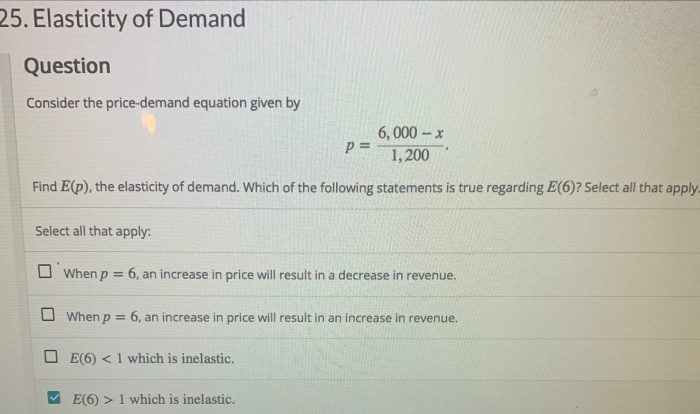
Elasticity
Elasticity measures the responsiveness of consumer demand to changes in prices or income. Price elasticity and income elasticity are important concepts for understanding how consumers react to market conditions.
4. Production and Costs
Factors of Production
The factors of production are the resources used in the production process, including land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship.
Types of Production Processes
There are various types of production processes, such as assembly lines, batch production, and continuous production, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Fixed and Variable Costs
Fixed costs are costs that do not change with the level of output, while variable costs vary with the level of output. Marginal cost is the change in total cost resulting from producing one additional unit of output.
Relationship between Production and Costs
The relationship between production and costs is crucial for firms to determine the optimal level of output and pricing strategies.
5. Perfect Competition
Characteristics of Perfect Competition
- Numerous buyers and sellers
- Homogeneous products
- Perfect information
- Freedom of entry and exit
Equilibrium in Perfect Competition
Equilibrium in a perfectly competitive market occurs when the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded, and the price is set at the intersection of the supply and demand curves.
Effects of Changes in Demand and Supply
Changes in demand or supply can shift the equilibrium price and quantity in a perfectly competitive market. Shifts in demand can lead to price and quantity adjustments, while shifts in supply can affect the equilibrium price.
6. Monopoly: Principles Of Microeconomics 10th Edition N Gregory Mankiw Free

Characteristics of Monopoly
- Single seller
- Unique product
- Barriers to entry
Profit-Maximizing Behavior of a Monopolist
A monopolist maximizes profits by setting a price above marginal cost and producing a quantity below the perfectly competitive level.
Welfare Effects of Monopoly
Monopoly can lead to market inefficiencies, higher prices, and reduced consumer welfare compared to perfect competition.
Government Policies to Address Monopoly Power
Governments may intervene to address monopoly power through antitrust laws, price regulations, and other measures.
7. Oligopoly and Monopolistic Competition

Characteristics of Oligopoly
- Few large firms
- Interdependence among firms
- Barriers to entry
Characteristics of Monopolistic Competition
- Many small firms
- Differentiated products
- Some market power
Pricing and Output Decisions in Oligopoly and Monopolistic Competition
Firms in oligopoly and monopolistic competition engage in strategic behavior to maximize profits, considering the reactions of their competitors.
8. Market Failures
Types of Market Failures
- Externalities
- Public goods
- Asymmetric information
Role of Government Intervention
Market failures can justify government intervention to improve market outcomes, such as through regulations, subsidies, or taxes.
Benefits and Costs of Government Intervention
Government intervention can have both benefits and costs, and the effectiveness of interventions depends on the specific market failure being addressed.
Essential FAQs
What is the main focus of Principles of Microeconomics, 10th Edition?
Principles of Microeconomics, 10th Edition focuses on the behavior of individual entities, such as consumers and firms, in the marketplace.
What are the key concepts covered in the book?
The book covers a wide range of microeconomic concepts, including market structures, consumer behavior, production and costs, perfect competition, monopoly, oligopoly, monopolistic competition, market failures, and government intervention.
Who is the author of Principles of Microeconomics, 10th Edition?
Principles of Microeconomics, 10th Edition is authored by N. Gregory Mankiw, a renowned economist and professor at Harvard University.