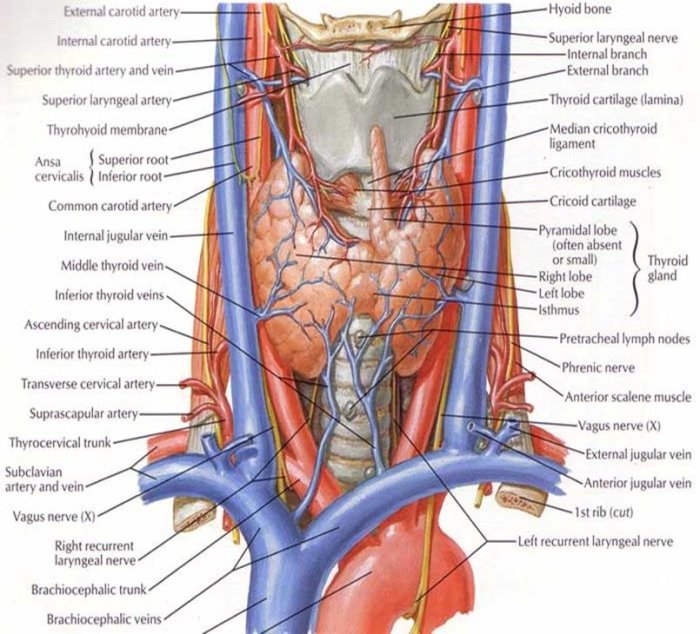
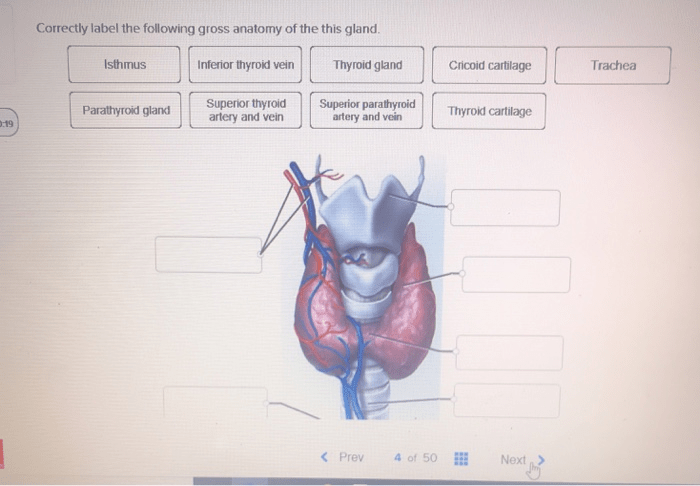
Correctly label the following gross anatomy of the gland – Correctly labeling the gross anatomy of the gland is a fundamental aspect of understanding its structure and function. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the techniques and methods used to accurately label the gland’s anatomy, ensuring a thorough understanding of this essential component of the human body.
The subsequent paragraphs delve into the various aspects of labeling the gland’s gross anatomy, including histological examination, imaging techniques, anatomical variations, and clinical implications. Additionally, educational resources are provided to enhance the learning experience and promote a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Gross Anatomy of the Gland
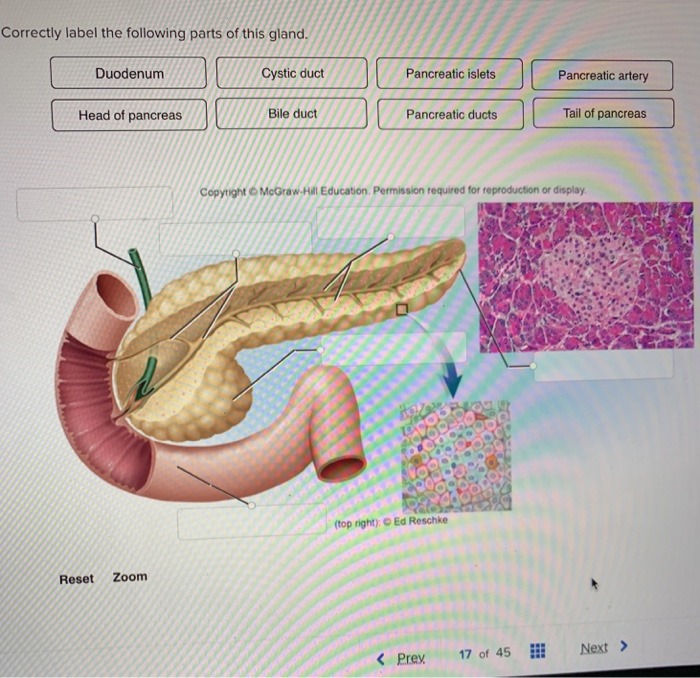
The gross anatomy of the gland encompasses the following structures:
- Lobes: The gland is divided into distinct lobes, each containing glandular tissue.
- Ducts: Ducts connect the lobes and transport secretions to the target organ.
- Capsule: A fibrous capsule surrounds the gland, providing structural support and protection.
- Hilum: The hilum is the point of entry for blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels.
Labeling Structure: Correctly Label The Following Gross Anatomy Of The Gland
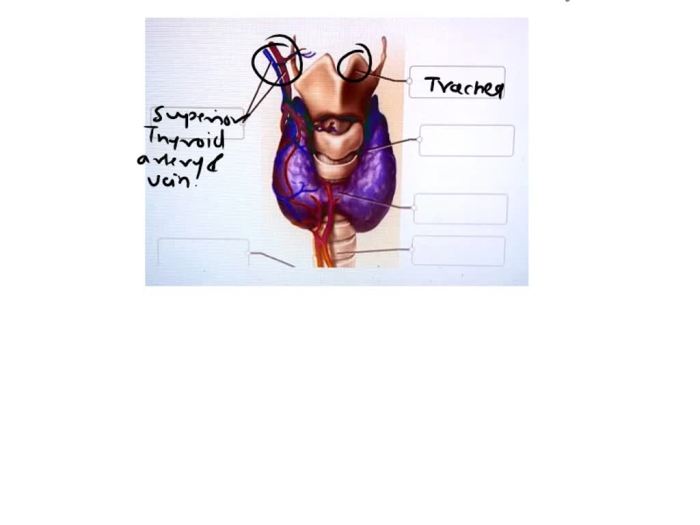
Accurate labeling of the gland’s gross anatomy is essential for precise communication and documentation. Standard labeling conventions include:
- Use anatomical terms that are universally recognized and unambiguous.
- Identify all structures clearly and consistently, avoiding ambiguous or confusing terminology.
- Orient the labels correctly in relation to the gland’s anatomical position.
- Label structures in a hierarchical manner, starting with the most general and progressing to the most specific.
Histological Examination
Histological examination involves the microscopic analysis of tissue samples to assess the gland’s cellular composition and architecture. Techniques include:
- Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining: This basic staining technique differentiates between cell nuclei and cytoplasm.
- Immunohistochemistry: Antibodies specific to particular proteins or markers are used to identify specific cell types or molecules.
- Electron microscopy: Provides ultrastructural details of the gland’s cellular components.
Imaging Techniques, Correctly label the following gross anatomy of the gland
Various imaging modalities allow for non-invasive visualization of the gland’s anatomy:
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the gland’s structure and blood flow.
- Computed tomography (CT): X-rays generate cross-sectional images of the gland, providing detailed anatomical information.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): Magnetic fields and radio waves create detailed images of the gland and its surrounding tissues.
Anatomical Variations
The gland’s anatomy can exhibit variations, including:
- Size and shape: The gland may vary in size and shape between individuals.
- Lobe number: The number of lobes can vary, with some individuals having accessory lobes.
- Ductal anatomy: The branching pattern and number of ducts can vary.
Clinical Implications
Accurate labeling of the gland’s anatomy is crucial for clinical practice:
- Surgical procedures: Precise identification of anatomical structures ensures safe and effective surgical interventions.
- Diagnostic imaging: Accurate labeling facilitates the interpretation of imaging studies, aiding in the diagnosis of diseases.
- Anatomical research: Standardized labeling enables the comparison of research findings and the advancement of medical knowledge.
Educational Resources
Numerous educational materials are available to facilitate learning about the gland’s anatomy:
- Textbooks: Comprehensive anatomy textbooks provide detailed descriptions and illustrations of the gland’s anatomy.
- Online resources: Websites and databases offer interactive models, simulations, and images for visualizing the gland’s anatomy.
- Atlases: Anatomical atlases provide high-quality images and diagrams of the gland’s gross and microscopic anatomy.
Expert Answers
What is the importance of correctly labeling the gross anatomy of the gland?
Correctly labeling the gross anatomy of the gland is essential for accurately identifying and describing its structures, facilitating effective communication among healthcare professionals, and ensuring precise surgical interventions.
What are the different labeling techniques used for the gross anatomy of the gland?
Various labeling techniques are employed, including descriptive terminology, anatomical landmarks, and histological staining methods, each providing a unique perspective on the gland’s anatomy.
How can imaging techniques assist in labeling the gross anatomy of the gland?
Imaging modalities such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans provide non-invasive visualization of the gland’s internal structures, aiding in the accurate labeling of its anatomy.