Chapter 4 ap stats practice test – Prepare for success on the Chapter 4 AP Statistics Practice Test with this comprehensive guide. This practice test covers a wide range of topics, including data analysis, probability, hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis. Whether you’re a student seeking to improve your test-taking skills or an educator looking for valuable resources, this guide provides essential insights and strategies for mastering the fundamentals of AP Statistics.
This practice test is designed to help you assess your understanding of the key concepts covered in Chapter 4 of the AP Statistics curriculum. By working through the practice questions and reviewing the answer keys and explanations, you can identify areas where you excel and pinpoint topics that require further study.
This targeted approach allows you to focus your preparation efforts and maximize your chances of success on the actual AP Statistics exam.
Introduction
The Chapter 4 AP Statistics practice test is designed to assess your understanding of the concepts covered in Chapter 4 of the AP Statistics curriculum. The test covers a range of topics, including:
- Sampling distributions
- Confidence intervals
- Hypothesis testing
By taking this practice test, you can identify areas where you need additional study and improve your overall understanding of the material.
Data Analysis
Data analysis is the process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, informing conclusions, and supporting decision-making.
There are two main types of data analysis: descriptive statistics and inferential statistics.
Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics summarize and describe the main features of a dataset. They provide a concise overview of the data and can help to identify patterns and trends.
- Measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode)
- Measures of variability (range, standard deviation, variance)
- Graphical representations (histograms, box plots, scatterplots)
Inferential Statistics
Inferential statistics use sample data to make inferences about a larger population. They allow researchers to draw conclusions about the population based on the data they have collected.
- Hypothesis testing
- Confidence intervals
- Regression analysis
Probability
Probability is a fundamental concept in statistics that measures the likelihood of an event occurring. It is expressed as a number between 0 and 1, where 0 indicates an impossible event, 1 indicates a certain event, and values between 0 and 1 represent varying degrees of likelihood.
Probability plays a crucial role in statistics, as it allows us to make inferences about populations based on samples and to quantify the uncertainty associated with our conclusions. It is used in a wide range of statistical applications, including hypothesis testing, confidence interval estimation, and regression analysis.
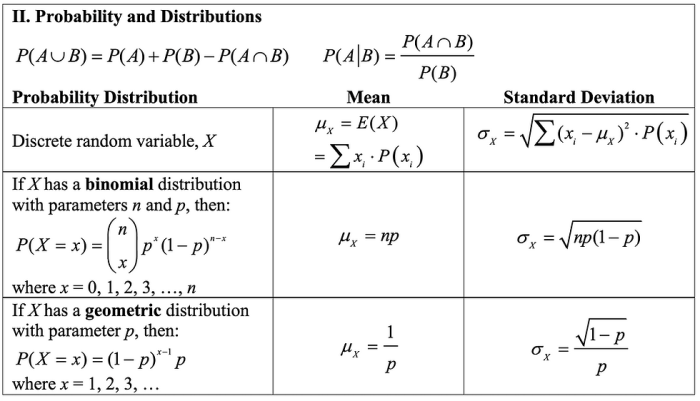
Probability Distributions
A probability distribution is a mathematical function that describes the probability of different outcomes in a random experiment. There are many different probability distributions, each with its own unique properties and applications.
- Normal distribution:The normal distribution, also known as the Gaussian distribution, is a bell-shaped distribution that is commonly used to model continuous data. It is characterized by its mean and standard deviation, which determine the center and spread of the distribution, respectively.
- Binomial distribution:The binomial distribution is a discrete distribution that is used to model the number of successes in a sequence of independent experiments, each of which has a constant probability of success. It is characterized by the number of trials and the probability of success on each trial.
4. Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to determine whether a hypothesis about a population parameter is supported by the available evidence from a sample. It involves making an initial assumption about the population parameter, called the null hypothesis, and then collecting data from a sample to test whether the data provides enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis.
The steps involved in hypothesis testing are as follows:
- State the null hypothesis (H0) and the alternative hypothesis (H 1).
- Set the significance level (α).
- Collect a sample from the population.
- Calculate the test statistic.
- Determine the p-value.
- Make a decision about the null hypothesis.
Types of Hypothesis Tests, Chapter 4 ap stats practice test
There are many different types of hypothesis tests, each designed to test a specific type of hypothesis. Some of the most common types of hypothesis tests include:
- One-sample t-testsare used to test hypotheses about the mean of a population when the population standard deviation is unknown.
- Two-sample t-testsare used to test hypotheses about the difference between the means of two populations when the population standard deviations are unknown.
- Chi-square testsare used to test hypotheses about the distribution of a categorical variable.
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA)is used to test hypotheses about the means of three or more populations.
Confidence Intervals
Confidence intervals are a statistical tool used to estimate the true value of a population parameter based on a sample. They provide a range of values within which the true parameter is likely to fall, with a specified level of confidence.
Confidence intervals are constructed using a variety of methods, including the t-interval and z-interval. The t-interval is used when the population standard deviation is unknown, while the z-interval is used when the population standard deviation is known.
Calculating Confidence Intervals
To calculate a confidence interval, we need the following information:
- The sample mean
- The sample standard deviation
- The desired confidence level
Once we have this information, we can use the following formula to calculate the confidence interval:
CI = x̄ ± z* (s/√n)
where:
- CI is the confidence interval
- x̄ is the sample mean
- s is the sample standard deviation
- n is the sample size
- z is the z-score corresponding to the desired confidence level
Interpretation of Confidence Intervals
Confidence intervals provide us with a range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to fall, with a specified level of confidence. For example, a 95% confidence interval means that we are 95% confident that the true population parameter falls within the calculated range.
Confidence intervals are a valuable tool for making inferences about population parameters based on sample data. They allow us to estimate the true value of a parameter with a known level of precision.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to investigate the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables. It is widely used in various fields, including economics, finance, social sciences, and natural sciences.Regression analysis aims to develop a mathematical model that describes the relationship between the variables.
This model can then be used to make predictions about the dependent variable based on the values of the independent variables.
Simple Linear Regression
Simple linear regression is the simplest type of regression model, involving only one independent variable. It assumes a linear relationship between the dependent and independent variables, represented by the equation y = a + bx, where y is the dependent variable, x is the independent variable, a is the intercept, and b is the slope.
Multiple Regression
Multiple regression is an extension of simple linear regression, involving multiple independent variables. It allows for the investigation of the combined effect of several independent variables on the dependent variable. The equation for multiple regression is y = a + b1x1 + b2x2 + … + bnxn, where y is the dependent variable, x1, x2, …, xn are the independent variables, a is the intercept, and b1, b2, …, bn are the slopes.
Practice Questions
Practice questions are an essential tool for preparing for the Chapter 4 AP Statistics Practice Test. By completing these questions, students can identify areas where they need additional review and gain confidence in their ability to apply the concepts they have learned.
The following practice questions cover the topics tested on the Chapter 4 AP Statistics Practice Test. Each question is followed by an answer key and explanation.
Hypothesis Testing
- A researcher wants to test the hypothesis that the mean weight of newborn babies is 7 pounds. A sample of 50 newborn babies has a mean weight of 6.8 pounds and a standard deviation of 1.2 pounds. Conduct a hypothesis test to determine if there is sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis.
- A company claims that their new coffee machine can produce a cup of coffee in less than 60 seconds. A sample of 20 cups of coffee produced by the machine has a mean time of 58 seconds and a standard deviation of 5 seconds.
Conduct a hypothesis test to determine if there is sufficient evidence to support the company’s claim.
Confidence Intervals
- A poll of 1000 voters found that 55% of voters support a particular candidate. Construct a 95% confidence interval for the proportion of voters who support the candidate.
- A company wants to estimate the mean salary of its employees. A sample of 50 employees has a mean salary of $50,000 and a standard deviation of $5,000. Construct a 90% confidence interval for the mean salary of all employees.
Regression Analysis
- A researcher wants to investigate the relationship between the number of hours a student studies and their final exam score. A sample of 10 students is collected, and the following data is recorded:
Hours Studied Final Exam Score 2 75 4 80 6 85 8 90 10 95 Calculate the least squares regression line for the data.
- A company wants to predict the sales of a new product based on the amount of money spent on advertising. A sample of 10 advertising campaigns is collected, and the following data is recorded:
Advertising Spending (in thousands) Sales (in units) 10 100 20 150 30 200 40 250 50 300 Calculate the correlation coefficient between advertising spending and sales.
Tips for Success

Preparing for the Chapter 4 AP Statistics practice test requires a strategic approach. By following these tips, students can enhance their preparation and improve their test-taking skills.
Strategies for Preparing
- Review course materials thoroughly, focusing on key concepts and formulas.
- Practice solving problems regularly to develop fluency and confidence.
- Attend review sessions or consult with teachers for additional support and clarification.
- Simulate test-taking conditions by practicing under timed conditions.
- Identify areas of weakness and focus on improving them through targeted practice.
Tips for Improving Test-Taking Skills
- Read instructions carefully and allocate time wisely for each section.
- Start with easier questions to build confidence and momentum.
- Show all work clearly and legibly, even for multiple-choice questions.
- Check answers thoroughly before submitting the test.
- Manage time effectively by skipping difficult questions initially and returning to them later if time permits.
Key Questions Answered: Chapter 4 Ap Stats Practice Test
What is the purpose of the Chapter 4 AP Statistics Practice Test?
The Chapter 4 AP Statistics Practice Test is designed to help students assess their understanding of the key concepts covered in Chapter 4 of the AP Statistics curriculum and identify areas where they need additional support.
What topics are covered on the Chapter 4 AP Statistics Practice Test?
The Chapter 4 AP Statistics Practice Test covers a wide range of topics, including data analysis, probability, hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis.
How can I use the Chapter 4 AP Statistics Practice Test to improve my score on the AP Statistics exam?
By working through the practice questions and reviewing the answer keys and explanations, you can identify areas where you excel and pinpoint topics that require further study. This targeted approach allows you to focus your preparation efforts and maximize your chances of success on the actual AP Statistics exam.