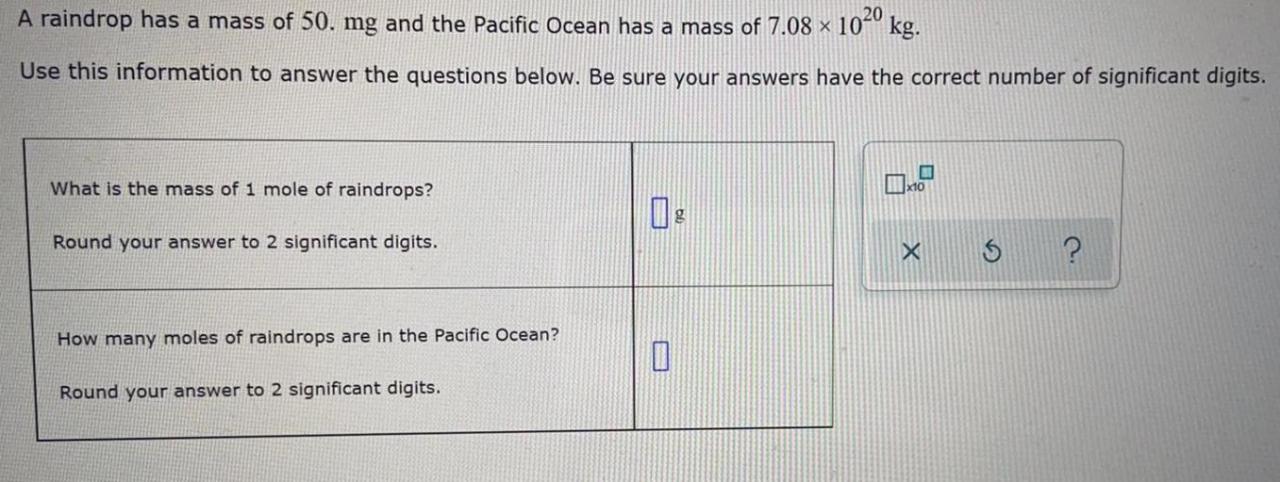
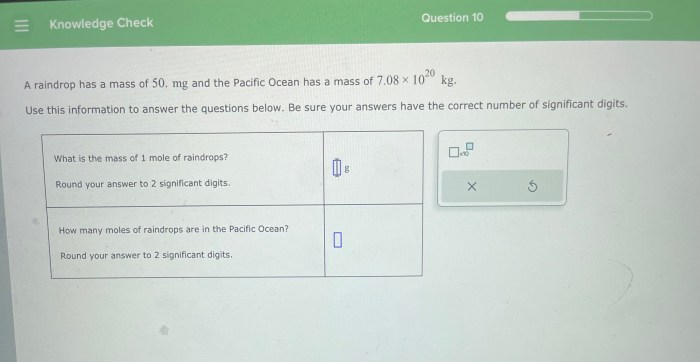
A raindrop has a mass of 50.mg – A raindrop has a mass of 50 mg, embarking us on a captivating journey into the realm of precipitation. This seemingly insignificant droplet holds a wealth of scientific intrigue, revealing the intricate interplay of mass, size, and atmospheric conditions that shape our weather patterns.
From the formation of clouds to the impact of raindrops on Earth’s ecosystems, the mass of a raindrop plays a pivotal role in understanding the delicate balance of our planet’s water cycle.
Mass of a Raindrop
Mass, in physics, refers to the quantitative measure of an object’s resistance to acceleration. It represents the amount of matter contained within an object and is a fundamental property that plays a crucial role in determining the behavior and interactions of objects.In
the context of raindrops, mass is particularly significant. Raindrops are formed through the condensation of water vapor in the atmosphere, and their mass is determined by the amount of water vapor that condenses. The mass of a raindrop is a key factor that influences its size, shape, and behavior as it falls through the atmosphere.
Formula for Calculating the Mass of a Raindrop, A raindrop has a mass of 50.mg
The mass of a raindrop can be calculated using the following formula:“`Mass = Volume × Density“`where:
- Mass is the mass of the raindrop in grams (g).
- Volume is the volume of the raindrop in cubic centimeters (cm³).
- Density is the density of water, which is approximately 1 g/cm³ at room temperature.
To calculate the mass of a raindrop, one needs to know its volume. The volume of a raindrop can be determined using its diameter and assuming it is a perfect sphere. The formula for the volume of a sphere is:“`Volume = (4/3) × π × (Diameter/2)³“`where:
- Volume is the volume of the sphere in cubic centimeters (cm³).
- π is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14.
- Diameter is the diameter of the sphere in centimeters (cm).
By combining these formulas, one can calculate the mass of a raindrop given its diameter.
Measuring Raindrop Mass
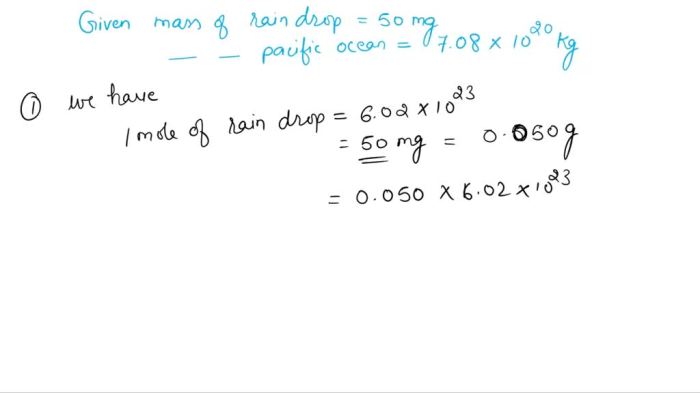
Determining the mass of a raindrop is a crucial step in understanding precipitation and atmospheric processes. Several methods have been developed to accurately measure raindrop mass, each with its own advantages and challenges.
Challenges in Raindrop Mass Measurement
Accurately measuring raindrop mass poses several challenges. Raindrops are often small and fragile, making it difficult to collect and handle them without altering their mass. Additionally, raindrops can vary significantly in size and shape, making it necessary to consider the effects of these variations on mass measurements.
Methods for Raindrop Mass Measurement
Despite these challenges, various methods have been developed to measure raindrop mass. These methods can be broadly classified into two categories: direct and indirect measurements.
- Direct Measurements:Direct measurements involve physically collecting and weighing raindrops. This can be done using a variety of instruments, such as:
- Disdrometer:A disdrometer uses a laser beam to measure the size and velocity of raindrops. The mass of the raindrop can then be calculated based on its size and density.
- Raindrop Collector:A raindrop collector is a device that collects raindrops on a filter paper or other surface. The mass of the raindrops can then be determined by weighing the filter paper before and after collection.
- Indirect Measurements:Indirect measurements infer the mass of raindrops based on their other properties, such as their size or velocity. These methods include:
- Radar Reflectivity:Radar reflectivity measurements can be used to estimate the mass of raindrops. Radar waves are reflected by raindrops, and the intensity of the reflected signal is proportional to the mass of the raindrops.
- Raindrop Size Distribution:Raindrop size distribution measurements can be used to estimate the mass of raindrops. By measuring the number of raindrops in different size ranges, the total mass of raindrops can be calculated.
Factors Affecting Raindrop Mass: A Raindrop Has A Mass Of 50.mg

The mass of a raindrop is influenced by several factors, including its size, density, and temperature. These factors interact in complex ways to determine the overall mass of a raindrop.
Raindrop Size
The size of a raindrop is a major factor that affects its mass. Larger raindrops have more water molecules and, therefore, a greater mass than smaller raindrops. The relationship between raindrop size and mass is not linear, however. As raindrops grow larger, they become less dense, which means that the increase in mass is not proportional to the increase in size.
Raindrop Density
The density of a raindrop is another important factor that affects its mass. Density is defined as the mass per unit volume. Raindrops are composed primarily of water, which has a density of 1 gram per cubic centimeter (g/cm 3) at room temperature.
However, the density of a raindrop can vary slightly depending on its temperature and the presence of impurities.
Raindrop Temperature
The temperature of a raindrop can also affect its mass. As the temperature of a raindrop increases, its density decreases. This is because the water molecules become more energetic and move further apart, resulting in a less dense raindrop.
Real-World Examples
The factors that affect raindrop mass can be seen in real-world examples. For instance, raindrops that form in warm, humid air tend to be larger and less dense than raindrops that form in cold, dry air. This is because the water vapor in warm, humid air is more likely to condense into larger droplets, and the higher temperature of the air causes the raindrops to be less dense.
Did you know that a raindrop typically weighs around 50 milligrams? That’s quite a bit of water! If you’re looking for more information on this topic, check out the unidad 3 lección 1 answer key . It’s a great resource for learning more about raindrops and other weather-related topics.
Returning to our original topic, a raindrop’s mass of 50 milligrams may seem small, but it can have a significant impact on the environment, contributing to plant growth and replenishing water sources.
Another example of how these factors can affect raindrop mass is the phenomenon of raindrops freezing. When raindrops freeze, they become more dense because the water molecules are packed more tightly together. This can cause the raindrops to fall more quickly and with greater force.
Significance of Raindrop Mass
Raindrop mass plays a pivotal role in comprehending precipitation dynamics. It influences rainfall intensity and duration, which are crucial factors in weather forecasting and hydrological modeling.
Rainfall Intensity
The mass of raindrops directly impacts rainfall intensity. Larger raindrops, with greater mass, fall faster due to increased gravitational pull. This results in heavier rainfall, leading to more significant accumulations in a shorter period. Conversely, smaller raindrops have less mass, causing them to fall more slowly and produce lighter rainfall.
Rainfall Duration
Raindrop mass also affects rainfall duration. Heavier raindrops tend to have shorter lifespans as they descend through the atmosphere. This is because they encounter more resistance from air molecules, causing them to evaporate or break up sooner. As a result, rainfall composed of larger raindrops is typically more intense but shorter in duration.
In contrast, smaller raindrops have longer lifespans, leading to rainfall that is less intense but more prolonged.
Weather Forecasting and Hydrological Modeling
Accurate measurements of raindrop mass are essential for weather forecasting and hydrological modeling. By understanding the distribution of raindrop sizes, meteorologists can better predict rainfall intensity and duration, improving the accuracy of weather forecasts. Hydrologists rely on raindrop mass data to estimate runoff and infiltration rates, which are crucial for flood control and water resource management.
Applications of Raindrop Mass Measurement
Raindrop mass measurement finds practical applications in various fields, including atmospheric research, climate studies, agriculture, and water resource management.
In atmospheric research and climate studies, raindrop mass data provides insights into cloud microphysics and precipitation processes. By measuring the mass distribution of raindrops, scientists can understand the formation and evolution of clouds, the efficiency of precipitation processes, and the impact of aerosols on cloud properties.
Role in Agriculture and Water Resource Management
In agriculture, raindrop mass measurement is crucial for understanding the impact of rainfall on crop growth and soil erosion. Large raindrops can cause significant damage to crops, while smaller raindrops are more beneficial for plant growth. By measuring raindrop mass, farmers can optimize irrigation practices and implement measures to mitigate the effects of heavy rainfall.
In water resource management, raindrop mass data is used to estimate rainfall intensity and predict runoff. Accurate rainfall measurements are essential for flood forecasting, reservoir management, and water conservation efforts.
FAQ Guide
How is the mass of a raindrop measured?
Raindrop mass is measured using specialized instruments such as disdrometers, which employ optical or electrical methods to capture the size and velocity of raindrops, allowing scientists to calculate their mass.
What factors influence the mass of a raindrop?
Raindrop mass is primarily influenced by its size, density, and temperature. Larger raindrops have greater mass, while denser raindrops (those with more water content) also weigh more. Temperature can also affect raindrop mass, as warmer temperatures lead to the evaporation of water, reducing the droplet’s mass.